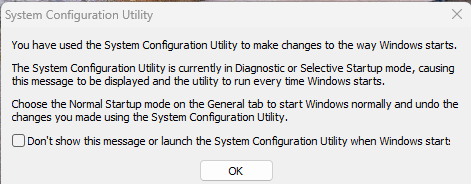
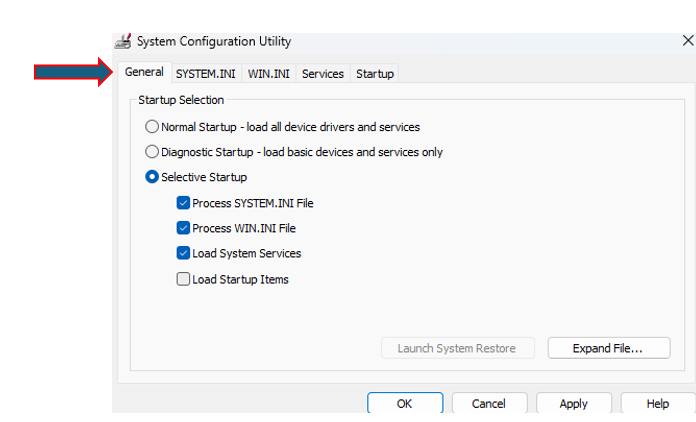
When your PC starts with a blue screen (often referred to as the “Blue Screen of Death” or BSOD), it typically indicates a critical system error. Here are some solutions you can take to troubleshoot and potentially fix the issue:
Solution 1: Restart Your Computer
Sometimes, a simple restart can resolve temporary issues.
Solution 2: Unplug all external devices and then start the PC.
The PC gets BSOD because of an external device.
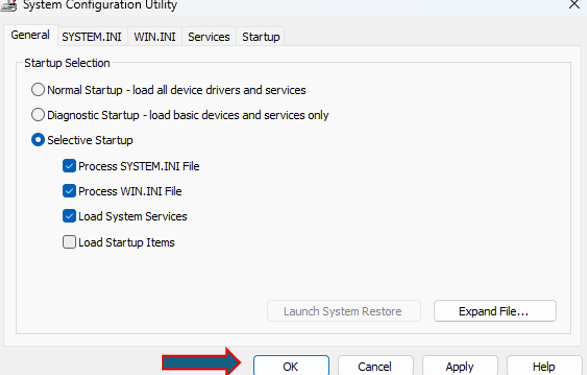
Solution 3: Boot into Safe Mode:
Restart your computer.
- Press
F8(orShift + F8) repeatedly before the Windows logo appears. - Select
Safe Modefrom the menu. - If your computer boots into Safe Mode, it indicates a software issue. You can then troubleshoot further from within Safe Mode.
Note: If Windows 11 boots too quickly for you to access Safe Mode using traditional methods, you can use solution 4, 5, 6.
Solution 4: Use the Power Button to interrupt the Boot Process
- Interrupt the Normal Boot Process:
- Turn on your computer.
- As soon as Windows starts to load, press and hold the power button for 10 seconds to force a shutdown.
- Repeat this process 2-3 times. On the third attempt, Windows should enter the Recovery Environment automatically.
2. Access Advanced Startup Options:
- Once in the Recovery Environment, you will see a screen with several options. Choose
Troubleshoot.
3. Navigate to Safe Mode:
- From the
Troubleshootmenu, go toAdvanced options>Startup Settings>Restart. - After your PC restarts, you’ll see a list of options. Press
4orF4to start in Safe Mode. If you need to use the Internet, press5orF5for Safe Mode with Networking.
Solution 5: Use a Windows Installation Media
- Create Windows Installation Media:
- Use another computer to create a Windows 11 installation USB drive using the Media Creation Tool from Microsoft’s website.
- Boot from USB:
- Insert the USB drive into your problematic PC.
- Restart the computer and boot from the USB drive. You may need to change the boot order in BIOS/UEFI to boot from the USB drive.
- Repair Your Computer:
- Select your language preferences, then click
Next. - Click
Repair your computerat the bottom left.
- Select your language preferences, then click
- Access Advanced Startup Options:
- From the
Choose an optionscreen, selectTroubleshoot>Advanced options>Startup Settings>Restart.
- From the
- Enable Safe Mode:
- After the restart, press
4orF4to start in Safe Mode. Press5orF5for Safe Mode with Networking if needed.
- After the restart, press
Solution 6: Use Command Prompt in Windows Recovery Environment
- Enter the Recovery Environment:
- Use the steps from Method 1 to force your PC into the Recovery Environment using the power button.
- Open Command Prompt:
- From the
Choose an optionscreen, selectTroubleshoot>Advanced options>Command Prompt.
- From the
- Enable Safe Mode:
- In the Command Prompt window, type the following command and press Enter:
bcdedit /set {default} safeboot minimal - For Safe Mode with Networking, use:
bcdedit /set {default} safeboot network - Close the Command Prompt and select
Continueto restart your PC. It will boot into Safe Mode.
- In the Command Prompt window, type the following command and press Enter:
Once your computer boots into Safe Mode, you can perform various troubleshooting steps to identify and resolve software issues. Here are some steps you can take:
1. Check for Malware
- Run Antivirus Software:
- Use your installed antivirus program to run a full system scan. If you don’t have one, you can use free tools like Malwarebytes.
- Download and install Malwarebytes, run a full scan, and remove any detected threats.
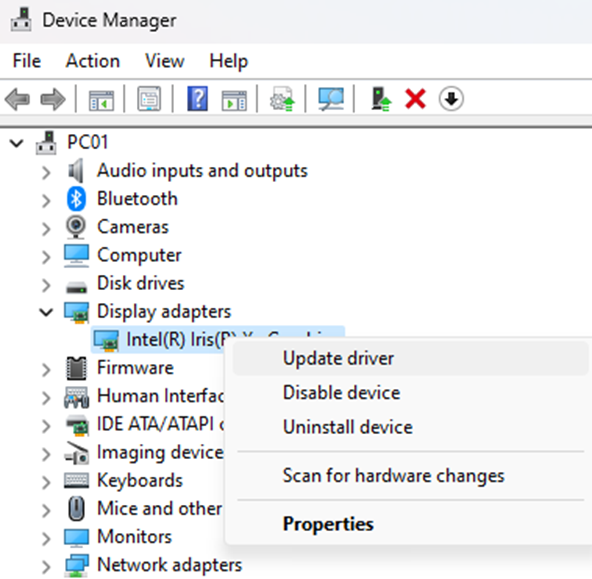
2. Update Drivers
- Open Device Manager:
- Press
Windows + Xand selectDevice Manager.
- Press
- Update Outdated Drivers:
- Look for any devices with a yellow triangle, indicating a problem.
- Right-click the device and select
Update driver. - Choose
Search automatically for updated driver software.
3. Uninstall Recently Installed Software
- Open Control Panel:
- Press
Windows + R, typecontrol, and press Enter.
- Press
- Uninstall Programs:
- Go to
Programs>Programs and Features. - Uninstall any recently installed software that might be causing issues.
- Go to
4. Run System File Checker (SFC) and DISM
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator:
- Press
Windows + Xand selectCommand Prompt (Admin)orWindows PowerShell (Admin).
- Press
- Run SFC:
- In the Command Prompt window, type the following command and press Enter:
sfc /scannow - Wait for the scan to complete and follow any prompts to fix issues.
- In the Command Prompt window, type the following command and press Enter:
- Run DISM:
- If SFC finds errors but cannot fix them, run the Deployment Imaging Service and Management Tool (DISM) with the following command:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
- If SFC finds errors but cannot fix them, run the Deployment Imaging Service and Management Tool (DISM) with the following command:
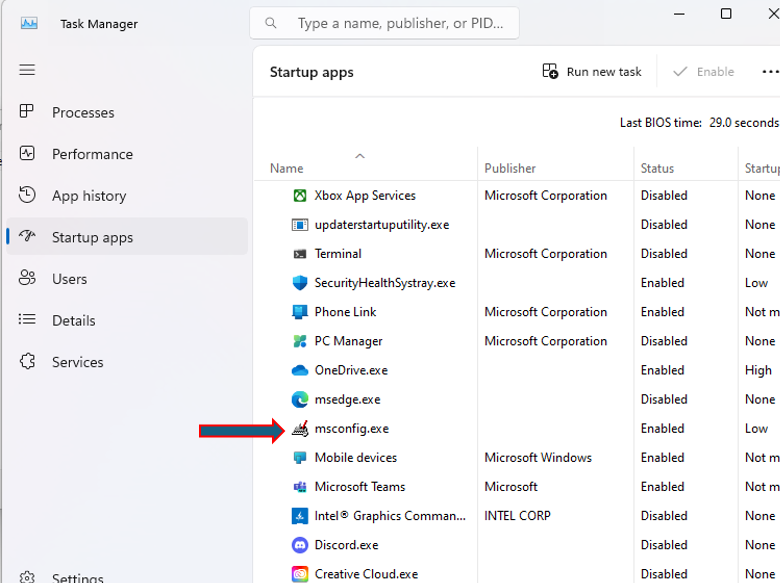
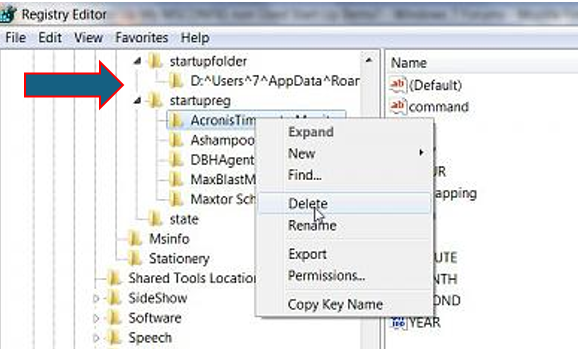
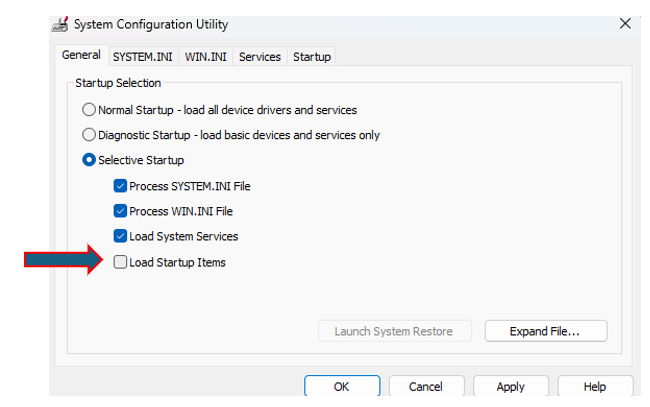
5. Disable Startup Programs
- Open Task Manager:
- Press
Ctrl + Shift + Escto open Task Manager.
- Press
- Disable Unnecessary Startup Programs:
- Go to the
Startuptab. - Right-click on any unnecessary programs and select
Disable.
- Go to the
6. Check Event Viewer for Errors
- Open Event Viewer:
- Press
Windows + Xand selectEvent Viewer.
- Press
- Look for Critical Errors:
- In the Event Viewer, navigate to
Windows Logs>System. - Look for any critical errors or warnings that might indicate the cause of the issue.
- In the Event Viewer, navigate to
7. Use System Restore
- Open System Restore:
- Press
Windows + R, typerstrui, and press Enter.
- Press
- Choose a Restore Point:
- Follow the prompts to choose a restore point before the issue started.
- Complete the restore process and restart your computer.
8. Reinstall Problematic Software
- Uninstall and Reinstall Software:
- If a specific software is causing the issue, uninstall it from
Control Panel>Programs>Programs and Features. - Restart your computer and reinstall the software.
- If a specific software is causing the issue, uninstall it from
9. Update Windows
- Check for Updates:
- Open Settings (
Windows + I), go toUpdate & Security>Windows Update. - Click
Check for updatesand install any available updates.
- Open Settings (
10. Check Disk for Errors
- Run Check Disk Utility:
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator (as described in step 4).
- Type the following command and press Enter:
chkdsk /f /r - You might need to restart your computer to complete the scan.
Additional Tips
- Backup Data: Always make sure your important data is backed up before performing major troubleshooting steps.
- Note Changes: Keep track of any changes you make during troubleshooting to easily revert if needed.
If you encounter specific issues or error messages while performing these steps, feel free to ask for more detailed assistance.